Die Casting Equipment
Die casting machines can be divided into two different types, hot chamber die casting machines and cold chamber die casting machines. The difference lies in how much force they can withstand. The typical pressure range is between 400 and 4000 tons.
Hot chamber die casting
Hot chamber die casting, sometimes called gooseneck die casting, has molten liquid and semi-liquid metal in the metal pool, which fills the mold under pressure. At the beginning of the cycle, the piston of the machine is in a contracted state, and the molten metal can fill the goose neck. Pneumatic or hydraulic pistons squeeze the metal and fill it into the mold. The advantages of this system include fast cycle speed (approximately 15 cycles per minute), easy automatic operation, and convenient metal melting process. Disadvantages include the inability to die-cast metals with higher melting points, as well as the inability to die-cast aluminum, because aluminum will take out the iron in the melting pool. Therefore, hot chamber die casting machines are generally used for alloys of zinc, tin and lead. Moreover, hot chamber die casting is difficult to die-cast large castings, usually this process is die-casting small castings.
Cold chamber die casting
Cold-chamber die-casting can be used when die-casting metals that cannot be used in the hot-chamber die-casting process, including aluminum, magnesium, copper, and zinc alloys with high aluminum content. In this process, the metal needs to be melted first in a separate crucible [2]. Then a certain amount of molten metal is transferred to an unheated injection chamber or nozzle. By hydraulic or mechanical pressure, these metals are injected into the mold. Due to the need to transfer the molten metal into the cold room, the biggest disadvantage of this process is the long cycle time. Cold chamber die casting machines are divided into vertical and horizontal types. Vertical die casting machines are usually small machines, while horizontal die casting machines have various models.
Mould
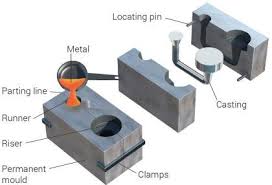
The die-casting mold is composed of two parts, the covering part and the movable part. The combined part is called the parting line. In hot chamber die casting, the covered part has a gate, while in cold chamber die casting it is an injection port. Molten metal can enter the mold from here, and the shape of this part matches the injection nozzle in hot chamber die casting or the injection chamber in cold chamber die casting. The movable part usually includes a push rod and a runner. The so-called runner is the channel between the gate and the cavity through which the molten metal enters the cavity. The covering part is usually connected to the fixed pressure plate or the front pressure plate, and the movable part is connected to the movable pressure plate. The cavity is divided into two cavity inserts, which are independent parts that can be removed or installed from the mold relatively easily by bolts.
The mold is specially designed so that the casting will remain in the movable part when the mold is opened. In this way, the push rod of the movable part will push the casting out. The push rod is usually driven by the pressure plate. It will accurately drive all the push rods at the same time with the same amount of force, so as to ensure that the casting is not damaged. When the casting is pushed out, the pressure plate shrinks to retract all the push rods to prepare for the next die casting. Since the casting is still in a high temperature state when it is demolded, only the number of push rods is large enough to ensure that the average pressure on each push rod is small enough to not damage the casting. However, the push rod will still leave traces, so it must be carefully designed so that the position of the push rod will not have too much influence on the operation of the casting.
Other parts in the mold include core slides and so on. Cores are parts used to make holes or openings in castings. They can also be used to increase the details of the casting. There are three main types of cores: fixed, movable and loose. The direction of the fixed core is parallel to the direction of the casting out of the mold. They are either fixed or permanently connected to the mold. The movable core can be arranged in any direction except the ejection direction. After the casting is solidified, before the mold is opened, the movable core must be taken out of the cavity by a separating device. The slider and the movable core are very close, the biggest difference is that the slider can be used to make an undercut surface. The use of cores and sliders in die casting will greatly increase costs. Loose cores are also called take-out blocks and can be used to make complex surfaces such as threaded holes. Before the start of each cycle, the slider needs to be manually installed, and finally pushed out together with the casting. Then take out the loose core. The loose core is the most expensive core because it requires a lot of labor to manufacture and it increases cycle time.
The discharge port is usually thin and long (about 0.13 mm), so the molten metal can be cooled quickly to reduce waste. There is no need to use a riser in the die-casting process, because the molten metal has a high pressure, which can ensure a steady flow from the gate into the mold.
Due to temperature, the most important material properties for molds are thermal vibration resistance and flexibility. Other features include hardenability, machinability, thermal crack resistance, weldability, and usability (especially for large molds) And cost. Mold life depends directly on the temperature of the molten metal and the time of each cycle. The mold used for die casting is usually made of hard tool steel. Because cast iron cannot withstand the huge internal pressure, the mold is expensive, which also leads to high mold opening costs. Die-cast metals at higher temperatures require the use of harder alloy steels.
The main defects that occur in the die casting process include wear and erosion. Other defects include thermal cracking and thermal fatigue. When the mold surface has defects due to too much temperature change, thermal cracks will occur. After too many uses, the defects on the mold surface will cause thermal fatigue.
The metals used for die casting mainly include zinc, copper, aluminum, magnesium, lead, tin and lead-tin alloys. Although die-cast iron is rare, it is also feasible. More special die-casting metals include ZAMAK, aluminum-zinc alloys and the standards of the American Aluminum Association: AA380, AA384, AA386, AA390 and AZ91D magnesium. The characteristics of various metals are as follows:
• Zinc: the easiest metal to die-cast. It is economical to manufacture small parts, is easy to coat, has high compressive strength, high plasticity, and long casting life.
• Aluminum: Lightweight, complex manufacturing and thin-walled castings have high dimensional stability, strong corrosion resistance, good mechanical properties, high thermal and electrical conductivity, and high strength at high temperatures.
• Magnesium: It is easy to be machined, has a high strength-to-weight ratio, and is the lightest among commonly used die-cast metals.
• Copper: High hardness, strong corrosion resistance, the best mechanical properties of commonly used die-casting metals, wear resistance, and strength close to steel.
• Lead and tin: high density, high dimensional accuracy, can be used as special anti-corrosion parts. For public health considerations, this alloy cannot be used as food processing and storage equipment. The alloy of lead, tin and antimony (sometimes containing a bit of copper) can be used to make manual type and bronzing in letterpress printing.
The upper mass limits for die-casting using aluminum, copper, magnesium and zinc are 70 lb (32 kg), 10 lb (4.5 kg), 44 lb (20 kg) and 75 lb (34 kg) respectively.
Pros and cons
advantage
The advantages of die casting include excellent dimensional accuracy of castings. Usually this depends on the casting material. The typical value is 0.1 mm for the initial 2.5 cm size, and 0.002 mm for each additional cm. Compared with other casting processes, its casting surface is smooth, and the fillet radius is about 1-2.5 microns. Compared to sandbox or permanent mold casting methods, castings with a wall thickness of about 0.75 mm can be produced. It can directly cast internal structures, such as wire sleeves, heating elements, and high-strength bearing surfaces. Other advantages include its ability to reduce or avoid secondary machining, fast production speed, casting tensile strength of up to 415 MPa, and the ability to cast high-fluidity metals.
Disadvantage
The biggest disadvantage of die casting is its high cost. Casting equipment, molds, and mold-related components are relatively expensive compared to other casting methods. Therefore, it is more economical to produce a large number of products when manufacturing die castings. Other disadvantages include: this process is only suitable for metals with high fluidity, and the casting quality must be between 30 grams and 10 kilograms [5]. In normal die casting, the last batch of castings always has porosity. Therefore, no heat treatment or welding can be performed, because the gas in the gap will expand under the action of heat, resulting in internal micro-defects and surface peeling.
Die casting is abbreviated as die casting. It is a casting method in which molten alloy liquid is poured into a press chamber, the cavity of a steel mold is filled at high speed, and the alloy liquid is solidified under pressure to form a casting. The main characteristics of die casting that distinguish it from other casting methods are high pressure and high speed.
①The molten metal fills the cavity under pressure, and crystallizes and solidifies under higher pressure, the common pressure is 15-100MPa.
②The molten metal fills the cavity at a high speed, usually 10-50 meters per second, and some can exceed 80 meters per second, (the linear velocity of the cavity through the inner gate-the inner gate speed), so the molten metal The filling time is extremely short, and the cavity can be filled in about 0.01-0.2 seconds (depending on the size of the casting).
Die casting is a precision casting method. Die castings made by die casting have very small dimensional tolerances and high surface accuracy. In most cases, die castings can be assembled and used without turning. Parts can also be cast directly. From small parts such as general camera parts, typewriter parts, electronic computing devices and decorations, as well as complex parts of vehicles such as automobiles, locomotives, and airplanes, most of them are manufactured by die casting.
Failure form
damage
During die-casting production, the mold is repeatedly stimulated by cold and heat, and the molding surface and its interior are deformed, and they are mutually involved, resulting in repeated cycles of thermal stress, resulting in damage to the structure and loss of toughness, causing the appearance of microcracks and continuing to grow. Once the crack expands, molten metal squeezes in, and repeated mechanical stresses accelerate the crack propagation. For this reason, on the one hand, the mold must be fully preheated at the beginning of die casting. In addition, the mold must be kept in a certain working temperature range during the die-casting production process to avoid early cracking failure. At the same time, it is necessary to ensure that the internal factors before and during the production of the mold do not cause problems. In actual production, most mold failures are thermal fatigue crack failure.
Shattered
Under the action of the injection force, the mold will initiate cracks at the weakest part, especially if the scribing marks or electrical machining marks on the molding surface of the mold are not polished, or the clear corners of the molding will first appear micro cracks , When there is a brittle phase or coarse grains at the grain boundary, it is easy to break. However, the crack propagation is very fast during brittle fracture, which is a very dangerous factor for the failure of the mold. To this end, on the one hand, all scratches and electrical machining marks on the mold surface must be polished, even if it is in the pouring system, it must be polished. In addition, the mold materials used are required to have high strength, good plasticity, good impact toughness and fracture toughness.
Dissolution
As mentioned earlier, the commonly used die-casting alloys include zinc alloy, aluminum alloy, magnesium alloy, and copper alloy, as well as pure aluminum die-casting. Zn, Al, and Mg are more active metal elements, and they have a good affinity with mold materials. Especially Al is easy to bite. When the mold hardness is high, the corrosion resistance is better, and if there are soft spots on the molding surface, the corrosion resistance is unfavorable.
There are many factors that cause mold failure, including external factors (for example, whether the casting temperature is high or low, whether the mold is preheated, how much water is sprayed, whether the tonnage of the die casting machine is matched, the die casting pressure is too high, the inner gate speed is too fast, and the cooling Water opening is not synchronized with die casting production, the type of casting material and the level of composition Fe, the size and shape of the casting, the wall thickness, the type of coating, etc.). There are also internal factors (such as the metallurgical quality of the material of the mold itself, the forging process of the blank, the rationality of the mold structure design, the rationality of the pouring system design, the internal stress generated during the processing of the mold machine (electrical processing), the heat treatment process of the mold, including Various matching accuracy and finish requirements, etc.). If there is an early failure of the mold, it is necessary to find out which internal or external causes to improve in the future. However, in actual production, dissolution is only a part of the mold. For example, the parts (core, cavity) that are directly washed by the gate are prone to corrosion, and the aluminum alloy is prone to sticking to the mold at soft hardness.

Scan to wechat:
